
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Optoelectronic Technology, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
2 School of Information and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, Hangzhou 310023, China
3 Center for Terahertz Research, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
4 e-mail: langtingting@zust.edu.cn
Lithium niobate’s substantial nonlinear optical and electro-optic coefficients have recently thrust it into the limelight. This study presents a thorough review of bound states in the continuum (BICs) in lithium niobate metasurfaces, also suggesting their potential for sensing applications. We propose an all-dielectric tunable metasurface that offers high factor resonances in the terahertz range, triggered by symmetry-protected BICs. With exceptional sensitivity to changes in the refractive index of the surrounding medium, the metasurface can reach a sensitivity as high as 947 GHz/RIU. This paves the way for ultrasensitive tunable terahertz sensors, offering an exciting path for further research.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(12): 2168
浙江科技学院信息与电子工程学院,浙江 杭州 310023
提出一种太赫兹(THz)超构材料的湿度传感器,可用于测量4%~76.1%范围内的空气湿度。该湿度传感器由周期排列的哑铃型不锈钢孔构成,其工作波段位于太赫兹波段。仿真结果表明,该传感器具有较高的折射率灵敏度。为进一步提高对湿度的灵敏度,还选择对水分子较敏感的丝素蛋白作为湿敏材料,将其涂覆于传感器表面。研究表明,该传感器的湿度灵敏度仿真和实验结果分别为0.20 GHz/%和0.11 GHz/%,高于已有报道的一些超构材料湿度传感器。
材料 超材料 湿度传感器 太赫兹 丝素蛋白 光学学报
2023, 43(19): 1916001
中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院,浙江 杭州 310018
为了拓展超材料在太赫兹波段的生物传感应用,设计了一种双开口环结构的太赫兹超材料生物传感器,通过两个等效电容电感(LC)谐振实现了高折射率灵敏度传感。首先,使用有限积分技术(FIT)数值计算了该传感器的太赫兹光谱,并对其进行了结构尺寸优化。然后,在传感器表面放置了一层折射率可变的分析物,通过对不同透射光谱的计算分析,验证了该传感器具备161.06 GHz/RIU(RIU为折射率单位)的折射率灵敏度和1.98的品质因素(FOM)值。最后,采用传统光刻技术和剥离工艺在石英衬底上制作铜金属结构,制备了该传感器,利用其对牛血清白蛋白(BSA)溶液进行了实际测试,实验得到传感灵敏度为59.02 GHz/(ng·mm-2)和检测下限为0.004 mg/mL。
传感器 生物传感器 太赫兹超材料 双开口环结构

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Centre for THz Research, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
High-Q metasurfaces have important applications in high-sensitivity sensing, low-threshold lasers, and nonlinear optics due to the strong local electromagnetic field enhancements. Although ultra-high-Q resonances of bound states in the continuum (BIC) metasurfaces have been rapidly developed in the optical regime, it is still a challenging task in the terahertz band for long years because of absorption loss of dielectric materials, design, and fabrication of nanostructures, and the need for high-signal-to-noise ratio and high-resolution spectral measurements. Here, a polarization-insensitive quasi-BIC resonance with a high-Q factor of 1049 in a terahertz all-silicon metasurface is experimentally achieved, exceeding the current highest record by 3 times of magnitude. And by using this ultra-high-Q metasurface, a terahertz intensity modulation with very low optical pump power is demonstrated. The proposed all-silicon metasurface can pave the way for the research and development of high-Q terahertz metasurfaces.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(12): 2743
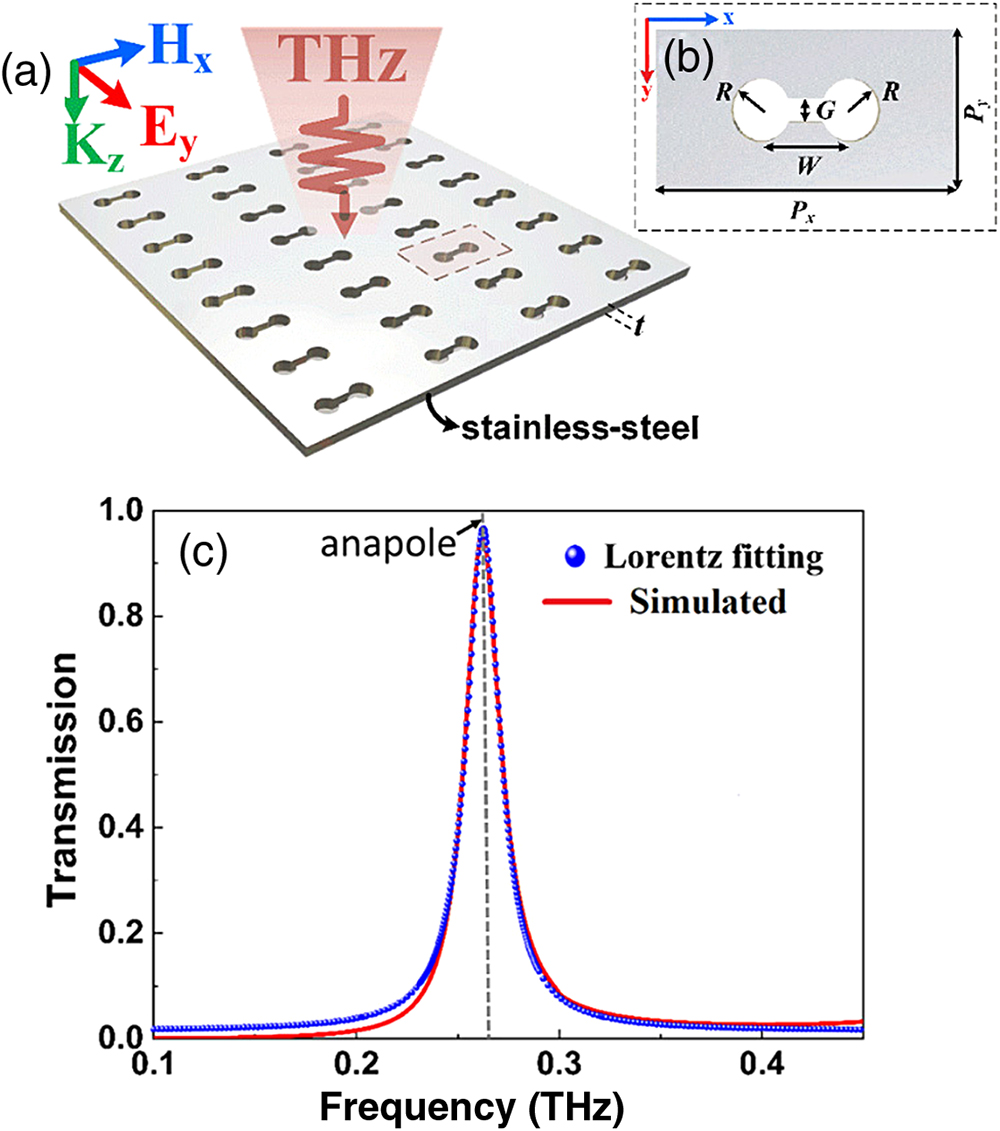
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Centre for THz Research, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
Anapole metamaterials have attracted growing attention in recent years due to their unique nonradiating and nontrivial properties. Although anapole modes have been demonstrated in metamaterials with three-dimensional structures, the design and realization of planar anapole metamaterials in a wide frequency range is still a big challenge. Here we propose and experimentally demonstrate a planar anapole metamaterial consisting of dumbbell-shaped apertures on a stainless-steel sheet at terahertz frequencies. The planar metamaterial can generate a resonant transparency in the terahertz spectrum due to the excitation of the anapole mode. Particularly, the frequency of anapole-induced resonant transparency can be tuned easily in the range of 0.15–0.93 THz by simply varying one geometric parameter of the dumbbell apertures. We anticipate that the resonant transparency in planar anapole metamaterials can be potentially used in filters, sensors, or other photonic devices.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(2): 02000125
1 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院现代光学仪器国家重点实验室, 集成光电子研究中心, 浙江 杭州 310027
2 中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院, 浙江 杭州 310018
通过在阵列波导的出口末端加入辅助波导,实现一种输入和输出通道数均为7(7×7),通道间隔为400 GHz的氮氧化硅阵列波导光栅路由器(AWGR),以提高损耗均匀性。利用引入的辅助波导调节在输出自由传输区的像平面处的场分布,通过优化其结构参数在像平面获得了平顶形状的场分布。与传统的AWGR相比,当光从中心输入通道输入时,带有辅助波导的AWGR所测得的输出损耗不均匀性从2.09 dB减少为0.76 dB;而当光从边缘输入通道输入时,输出通道输出的损耗不均匀性从1.99 dB降低为0.88 dB,可满足实际光通信、光互连等系统的需求。由于辅助波导的引入,中心通道的最小插入损耗从2.99 dB增加为3.82 dB,边缘通道的最小插入损耗从4.83 dB增加为5.46 dB。所有通道的串扰约为18 dB。
光学器件 波导 光栅 集成光学器件 导波应用 光学学报
2019, 39(11): 1123001
1 浙江大学光电科学与工程学院, 浙江 杭州 300027
2 中国计量大学光学与电子科技学院, 浙江 杭州 300027
设计并制作了一种全集成的基于波长路由的光真延时(OTTD)模块。该模块由两个相同的通道间隔为1.6 nm的16×16阵列波导光栅路由器(AWGR)与一组波导延时线阵级联而成。测试结果表明该模块性能优异,工作波长通道间串扰小于-27 dB,光纤端到端峰值波长的插入损耗约为12 dB。采用矢量网络分析仪测试得到延时线阵提供的光延时步长为(6.24±0.4) ps。该模块中两个阵列波导光栅路由器及延时线阵均被集成在一块硅基片之上,并且都由二氧化硅(SiO2)波导制作而成,整个器件尺寸为3.5 cm×3.5 cm。
光学器件 集成光器件 光真延时 光控相控阵雷达 阵列波导光栅路由器
中国计量学院光电子技术研究所, 浙江 杭州 310018
提出了一种基于高双折射光子晶体光纤(PCF)的偏振器件。通过引入包层缺陷结构,利用谐振耦合原理,实现在1250~1850 nm 波长范围内获得具有单一偏振模式的光子晶体光纤偏振器件,并且实现了在该波长范围内23~250 dB 的消光比。
光纤光学 偏振器 有限元法 光子晶体光纤 激光与光电子学进展
2014, 51(6): 060601





